Transfer data at scale from your warehouse to MinIO
Supported syncing
| Object Type | Description | Supported Sync Modes |
|---|---|---|
| Any data set | Sync data from a source to MinIO as CSV, JSON, or Parquet files | Insert, All, Diff |
- All: All mode creates one file with all the rows in the query results, every time the sync runs.
- Insert: Insert mode creates one file with the rows that were added since the last sync.
- Diff: Creates three files, one for rows added, one for rows changed, and another for rows removed since the last sync.
For more information about sync modes, refer to the sync modes docs.
The order of rows in uploaded files may differ from how they appear in your model. This is expected behavior and applies to all sync modes. Learn more about row ordering →
Prerequisites
To get started, you need:
- a MinIO bucket
- MinIO access key and secret key for use by Hightouch
Connect to MinIO
Go to the Destinations overview page and click the Add destination button. Select MinIO and click Continue. You can then authenticate Hightouch to MinIO by entering your Bucket Name. The Bucket Name should just be the name of the bucket, not a URL.
Sync configuration
Once you've set up your MinIO destination and have a model to pull data from, you can set up your sync configuration to begin syncing data. Go to the Syncs overview page and click the Add sync button to begin. Then, select the relevant model and the MinIO destination you want to sync to.
Select file format
Hightouch supports syncing JSON, CSV, and Parquet files to Amazon MinIO.
Enter filename
The filename or object key field lets you specify the parent directory and the name of the file you want to use for your results.
You can include timestamp variables in the filename, surrounding each with {}.
Hightouch supports these timestamp variables:
YYYY: Represents the full year in four digits.YY: The last two digits of the year.MM: Two-digit month format (01-12).DD: Two-digit day format (01-31).HH: Two-digit hour format in 24-hour clock (00-23).mm: Two-digit minute format (00-59).ss: Two-digit second format (00-59).ms: Three-digit millisecond format.X: Unix timestamp in seconds.x: Unix timestamp in milliseconds.
All dates and times are UTC.
For example, you could enter upload/{YYYY}-{MM}-{DD}-{HH}-{mm}-result.json to dynamically include the year, month, date, hour, and minute in each uploaded file.
Hightouch would insert each file in the upload directory, which would need to already exist in your bucket.
You can also use other variable values to include sync metadata in the filename:
{model.id}{model.name}{sync.id}{sync.run.id}
If a file already exists at the path you entered at the time of a sync, Hightouch overwrites it. To keep different versions of the same results file, you can enable versioning in your bucket, or your app can copy the data to another location.
{model.name}.Set filename offset
By default, Hightouch uses the timestamp of the sync run to fill in timestamp variables. You can optionally include an offset in seconds. For example, if you want the filename's date to be 24 hours before the sync takes place, enter -86400 (24 hours * 60 minutes * 60 seconds). If you want the filename's data to be one hour after the sync takes place, you would enter 3600 (60 minutes * 60 seconds).
CSV options
If you're syncing to a CSV file, you have additional configuration options:
- Delimiter: Your options are comma (
,), semicolon (;), pipe (|), tilde (~), and tab - (Optional) Whether to include a CSV header row in the exported files
- (Optional) Whether to include a byte order mark (BOM) in the exported files, the BOM is
<U+FEFF>
Columns to sync
You can export all columns exactly as your model returns them or choose to export specific ones.
If you need to rename or transform any column values you're syncing, you can use the advanced mapper to do so. If you choose this option, Hightouch only syncs the fields you explicitly map.
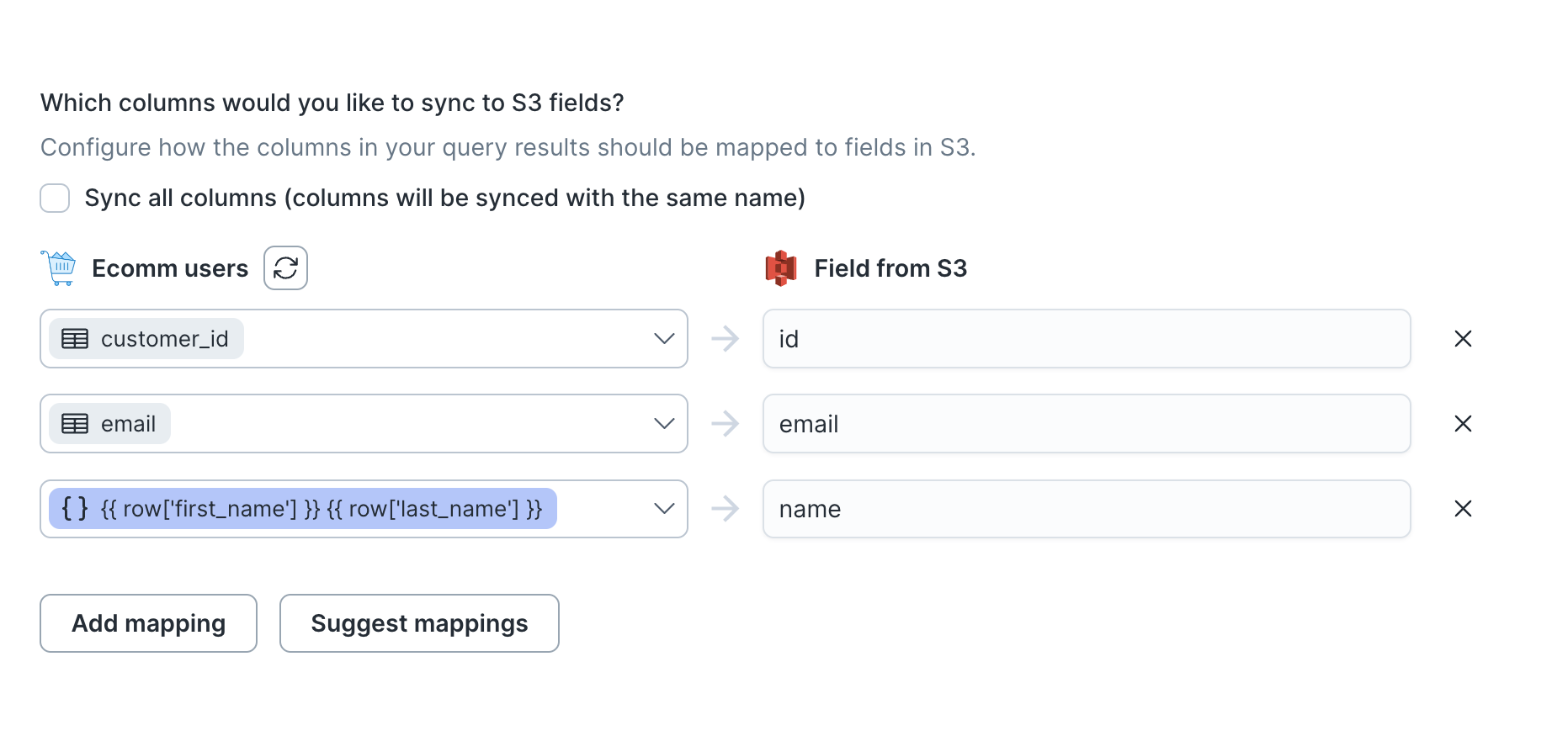
The preceding example shows how to selectively export the customer_id, email, first_name and last_name, columns. These columns are mapped to new fields in the destination file as id, email, and name—a templated concatenation of first_name and last_name—respectively. Hightouch exports these fields to new fields in the file and ignores all other columns from your results.
Batch size
By default, and depending on your sync mode, Hightouch sends one file to your MinIO bucket for each export. (In diff mode, Hightouch sends three files.)
By enabling batching, you allow Hightouch to send multiple files if your model query results are large. This can help avoid file size errors from MinIO.
Empty file results
You can select how Hightouch should handle empty results files. Empty result files can occur if your model's query results haven't changed since the last sync.
You can select whether to skip empty files. If you skip empty files, it means Hightouch won't export any files if your model's query results haven't changed since your last sync.
Gzip compression
You can enable gzip compression to reduce the size of your exported files. Note
that Hightouch does not automatically add the .gz extension to your files. You
can add this or any other extension to your filename.
Tips and troubleshooting
Common errors
If you encounter an error or question not listed below and need assistance, don't hesitate to . We're here to help.
Access denied
The ACCESS_DENIED error is a permissions-related error. Ensure the crendtials in Hightouch match the credentials used during MinIO setup.
Sync alerts
Hightouch can alert you of sync issues via Slack, PagerDuty, SMS, or email. For details, please visit our article on alerting.
